In modern financial life, a cash card is indispensable.
Issued by banks and credit unions, this card allows easy access to your deposit account, making it convenient to withdraw or deposit cash at ATMs and perform other basic transactions.
This article explains everything from the basics of cash cards, their types, how to obtain one, how to manage PINs, what to do if lost, differences from other cards, how to choose one, and even how to use them overseas.
We hope this serves as a helpful reference for safe and smart usage.
What Is a Cash Card?
A cash card is a plastic card linked to a bank account, issued by banks and credit unions.
With an ATM, you can withdraw or deposit cash even outside banking hours, making daily transactions more convenient.
Main Functions and Role
The main functions are cash withdrawals, deposits, and balance checks at ATMs.
Insert the card, enter your PIN, and you can access your funds easily. Some banks also allow balance inquiries through internet banking.
This eliminates the need to always carry cash, improving both convenience and safety.
The role of a cash card is to provide secure money management, reducing the risks of carrying large sums of cash. It also acts as a means of identity verification at ATMs, enabling access to funds anytime and anywhere without visiting a counter.
In addition, cash cards are increasingly integrated with online banking, serving as a gateway to digital services. They may evolve into access keys for broader online functions. With growing security awareness, reducing the risks of carrying cash has made cash cards even more essential.
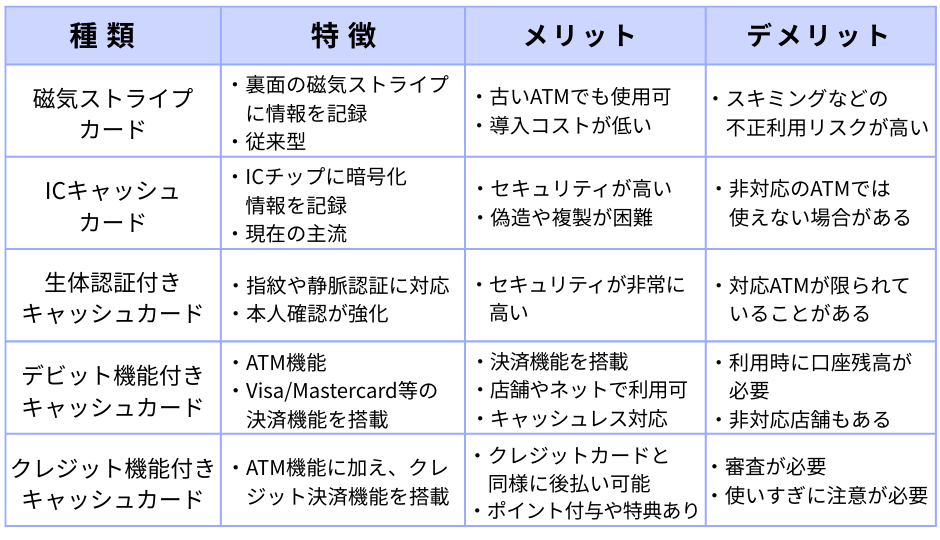
Types of Cash Cards
There are two main types: IC chip cards and magnetic stripe cards. Recently, biometric authentication cards, multi-function cards integrated with debit cards, and even credit card-integrated cash cards have also been introduced.

How to Get a Cash Card
Generally, you apply for a cash card when opening a bank account. The procedure involves filling out an application and presenting identification documents. Some banks let you choose between an IC card and a magnetic stripe card.
If you already have an account, you can apply through a branch, online banking, or by phone. Choose the method that suits you best.
Required Documents
Identification such as a driver’s license or My Number card is required. Some banks may also ask for proof of address or a personal seal. Always confirm in advance.
PIN for a Cash Card
A PIN is an important security measure for verifying your identity at ATMs. Proper management is required.
How to Set a PIN
After receiving your card, set a 4-digit PIN at an ATM menu. Some banks also allow setting it online. Never share your PIN with others.
How to Change Your PIN
You can change your PIN at any time via an ATM. Enter your current PIN and a new one. Some banks may limit the number of changes allowed.
What to Do If You Forget Your PIN
If forgotten, visit your bank branch with ID for a reset or reissue. For security, banks will not tell you your PIN over phone or online.
If You Lose Your Cash Card
If lost or stolen, immediate action is required. Contact your bank right away. Most banks provide 24-hour hotlines.
Process
The bank will confirm your details and proceed to suspend the card and issue a replacement. The new card will be mailed to your registered address.
Preventing Unauthorized Use
Until reissued, check your account frequently for suspicious activity. Use security services such as SMS alerts or withdrawal limits if available.
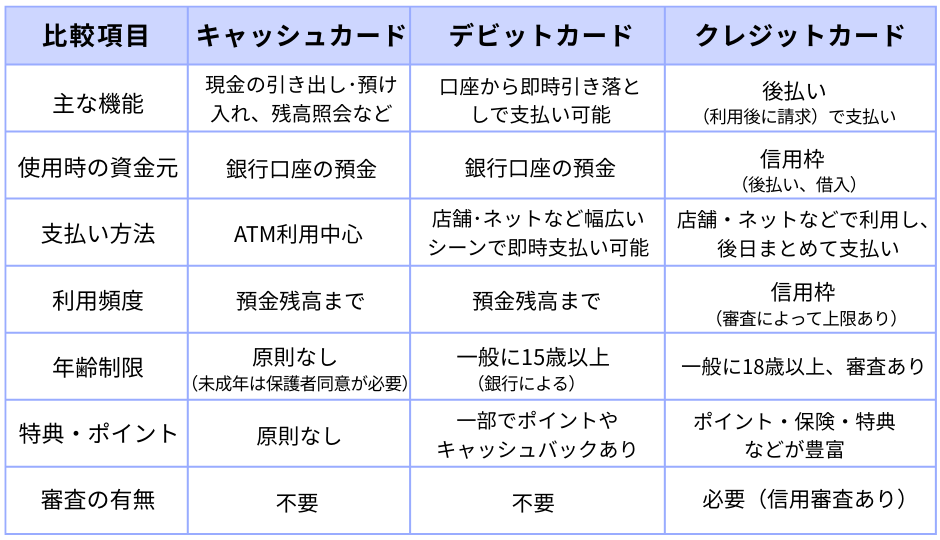
Cash Cards vs Other Cards
Besides cash cards, there are debit cards and credit cards. Each has different functions and uses. Understanding the differences helps you use them wisely according to your lifestyle.

Choosing a Bank
When choosing a bank (and its cash card), consider your usage habits and goals. The following points can help you choose wisely.
ATM Fees
Some banks charge fees depending on time or location. Frequent ATM users should choose a bank with many free withdrawals or nearby ATMs.
Reward Programs
Some banks offer reward points for account usage, which can be exchanged for vouchers or benefits. Compare programs if rewards are important to you.
Other Services
Also consider transfer fees, online banking features, loan availability, and investment products when choosing a bank.
Using a Cash Card Abroad
Most Japanese cash cards cannot be used overseas. However, some banks issue international debit or cash cards (linked with Visa or Mastercard) that can.
Overseas Availability
Check with your bank before traveling whether your card can be used abroad. Confirm supported ATMs and terms of use.
Overseas Fees
When used abroad, ATM usage fees and foreign exchange fees apply. Costs vary by country, ATM, and bank. Always confirm details in advance.
Summary
This article covered what cash cards are, their types, how to get one, how to use them safely, differences from other cards, choosing a bank, overseas usage, payments, auto-debit settings, age requirements, and security tips.
Cash cards are indispensable tools for managing money safely and conveniently. By understanding their features and precautions, you can use them wisely to support your financial life.
As financial technology evolves, cash cards are expected to integrate more advanced features such as biometrics and smartphone connectivity. Keep an eye on these developments and use cash cards smartly to ensure a safe and convenient financial life.